Using the Arduino IDE for esp32
Using the Arduino IDE for esp32
The ESP32 processor is not natively incuded in the Arduino IDE (Interactive Development Environment) when it is first downloaded. To include it, the ESP32 boards need to be added to the the IDE.
- Update preferences:
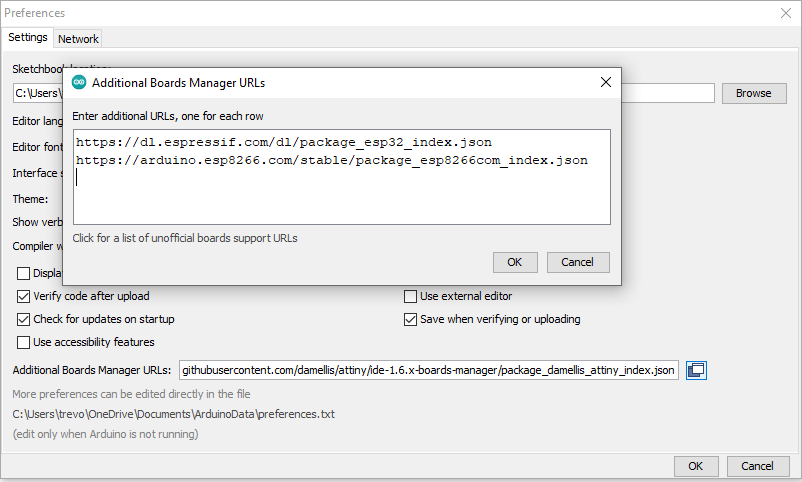
Under the menu option "Files", "Preferences" find the " Additional Boards Manager URLs", add the support for the ESP32 and additionally the esp8266 if required.
Use the icon on the right of the field to get the multi line input window and add one URL per line.
Multiple URLs can be added, also add any other architectures you may be interested in, eg:
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json https://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/damellis/attiny/ide-1.6.x-boards-manager/package_damellis_attiny_index.json
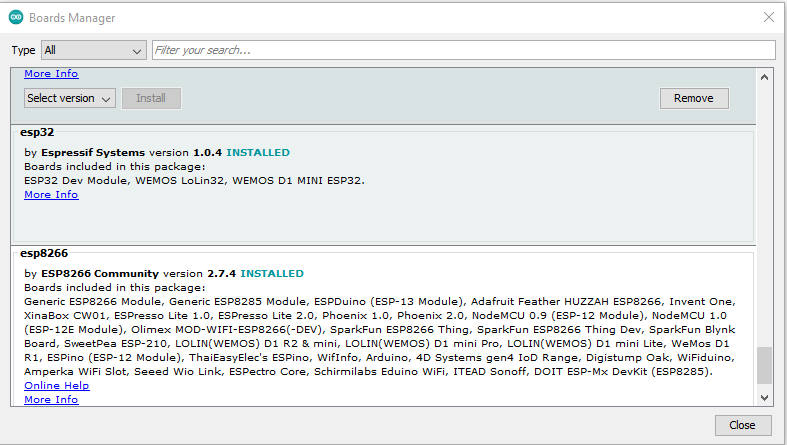
- Update boards manager: Depending on the speed of your connection, this step can take a while to complete as it needs to download about 125 Mbyte of board information.
Using the menus select "Tools", "Board <current-board-name>", "Boards Manager".
Scroll to the end of the list, and support for your additional architectures as selected in the previous step will appear, install the boards as required.
- Optionally add debugger support:
If you are developing your own code more complex than the "blinky" sketch, you are likely to encounter crashed sketches with stack tracebacks.
These stack tracebacks are not too meaningful, unless you can trace back where in the sketch the error occurred.
The "ESP Exeception decoder project provides just such a decoder.
Once installed it will appear under the "Tools", "ESP exception Decoder" menu option.
Depending on your computer's operating system, the "home" directory/folder may vary. For Windows users, look at the following locations for your "Arduino" project folder:
C:\Users\<your-userid>\OneDrive\Documents C:\Users\<your-userid>\Documents
- Other plug-ins: These may include plugins to upload files to a SPIFFS filesystem on esp32 board. The installation of these is similar to the decoder and the directory in the zip file is placed in the same tools sibdirectory.
Linux considerations
On Linux the compiler would not run unless Python serial support was installed and the user has access to the tty USB device(s). Using Ubuntu 22.04, the following commands were used to achieve this:
sudo apt-get install python-is-python3 sudo python -m pip install pyserial sudo usermod -a -G dialup username
When testing on a Linux machine, the serial port to a cp210x USB serial adapter would be discovered and then removed. It appeared the Braille reader was conflicting with the USB cp21x driver, and once that had been uninstalled the serial port worked well.
discovering the serial port being dropped:
sudo dmesg ... [ 581.956292] usb 1-1.2: USB disconnect, device number 5 [ 588.268525] usb 1-1.2: new full-speed USB device number 6 using ehci-pci [ 588.416372] usb 1-1.2: New USB device found, idVendor=10c4, idProduct=ea60, bcdDevice= 1.00 [ 588.416395] usb 1-1.2: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 [ 588.416403] usb 1-1.2: Product: CP2102 USB to UART Bridge Controller [ 588.416410] usb 1-1.2: Manufacturer: Silicon Labs [ 588.416416] usb 1-1.2: SerialNumber: 0001 [ 588.431040] cp210x 1-1.2:1.0: cp210x converter detected [ 588.432368] usb 1-1.2: cp210x converter now attached to ttyUSB0 [ 593.133733] usb 1-1.2: usbfs: interface 0 claimed by cp210x while 'brltty' sets config #1 [ 593.135579] cp210x ttyUSB0: cp210x converter now disconnected from ttyUSB0 [ 593.135664] cp210x 1-1.2:1.0: device disconnected
solution to remove Braille reader
udo apt-get remove brltty
| Thank you for visiting camelthorn.cloud | Home |